Data Center Infrastructure: Traditional vs Converged Infrastructure
Data Center Infrastructure (Part 2):
When we discuss Data Center Infrastructure, we hear the terms like Traditional Infrastructure, Converged Infrastructure (CI), and Hyper-Converged Infrastructure (HCI) etc. but what does it all mean? and what are the benefits of one over the other? Let’s take a look at each type of Data Center Infrastructure in order.
Traditional Infrastructure
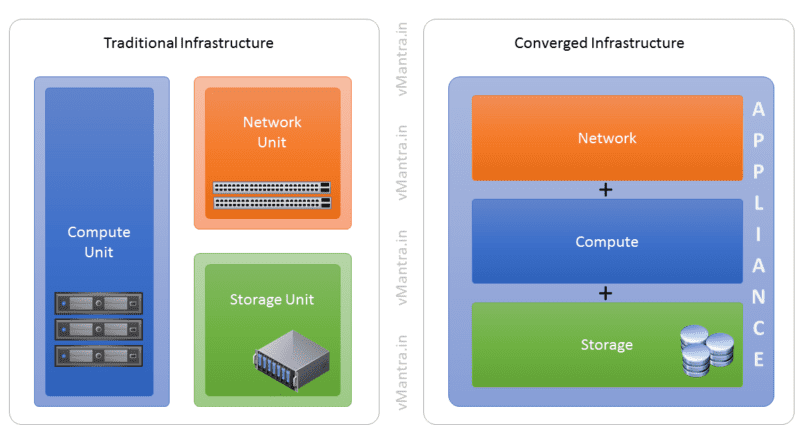
Let’s start with Traditional Data Center Infrastructure on which a large number of organizations still operate. Traditional Data Centers have been constructed with the hardware dedicated for a specific purpose. For example, a server can be used only for computing purposes and not for storage, and there are dedicated types of equipment for networking purposes that can not be used for other purposes. Each component works within an isolated layer having its own separate management. This means that to manage each kind of hardware, we need a dedicated team with a specific skill set. For example, there must be at least 3-4 separate teams for managing storage, servers, and networking. Also, a few more cross-functional teams may be required to work with other infrastructure layers like virtualization, security etc. Also, there must be a team that can track the warranty of different purchases from different vendors.
Assembling all these pieces of a traditional infrastructure results in complex Deployment, Operations & Management, and slower delivery of IT services and applications. This kind of environment is not even expensive but difficult to scale and requires specialized skill sets that are hard to find and harder to replace.
Various kinds of Hardware, Firmware, and Software require multiple teams and makes the process very complex which results in tons of coordination with tedious management.
Traditional Infrastructure has been in place when virtualization did not even exist. In those times It could be simply described as one application per physical server. But the advent of virtualization changed the way Traditional Datacenters were perceived.

Converged Infrastructure
Converged Infrastructure (CI) or Converged Architecture is a type of Data Center Infrastructure that aims to maximize the compatibility between computing, storage, and networking devices by introducing the concept of an appliance. These hardware appliances are pre-integrated smaller units combining compute, storage, and network in a single node. But in most of the cases, Converged Infrastructure is represented as a single hardware unit containing Compute and Storage functionality. This gives an easy path to resource augmentation and also easier to manage than Traditional Infrastructure. If we need to scale out, just add more appliances, and you are done. But still, each of the components can be used for its intended purpose. For example, the server and storage can be separated and use as two functional units.
CI are pre-defined for specific purposes and typically used for applications such as ERP, CRM, database grids, SAP workloads, and enterprise messaging.
This infrastructure is a combination of existing products and does not build on a new kind of hardware. It means there is no huge improvement in performance. But on the other hand, there are many benefits that can not be overlooked as:
Reduce Complexity: It offers a reduced footprint and less cabling and can be deployed much faster than traditional infrastructure.
Easy to Deployment: Buying a Converged Infrastructure node means buying Compute, Storage and Network units at one go. This makes the procurement team’s work hassle-free.
Better Management: Some solutions come with administration tools that can manage the entire environment, better management, and simplified procurement.
Easy to Procurement: Buying a Converged Infrastructure node means buying Compute, Storage, and Network units at one go. This makes the procurement team’s work hassle-free.
Improve Team Productivity: Deploying Converged Infrastructure means you can focus on maximizing your use of that environment instead of worrying about whether the various hardware silos will inter-operate with one another.
Even after many good features, Converged Infrastructure is still a hardware-focused solution. It could not provide the flexibility that is required to cope with current industry challenges.
The examples of Converged Infrastructures are VCE, Cisco UCS, Dell EMC VxBlock, and Pure Storage FlashStack.
Next Step
In the next blogs of this Data Center Infrastructure series, we will focus on Hyper-Converged Infrastructure and Composable Infrastructure along with some detailed information on Software-Defined Data Centers (SDDC). To know more please stay in touch.
Thanks!!
Check out some more blogs:
- Configuring AWS Greengrass Core on VMware vSphere
- Deploying AWS Greengrass on VMware vSphere
- VNF Manager vs NFV Orchestrator (VNFM vs NFVO)
- Network Functions Virtualization (NFV)
- What is Hyper-Threading?
- Virtual Networking in VMware Workstation
- Hyper-converged Archives
- vFORUM 2017 Recap
- Digital Voice Assistants
- Top SDN Vendors and their Solutions
If you like my blogs Please Share…
–
Shahzad
ref: wiki
hci vs traditional comparison, hyperconverged infrastructure data centers, hyperconverged vs converged, hyperconverged vs traditional, storage arrays, storage resources, automated storage provisioning, data center management